News
IMPORTANT NOTICE: New EU laws to protect member data are wide ranging and will affect your business
The lawmakers in the European Union have had enough.
Large firms reckless approach to security of data is going to be punished by massive fines of up to €20 million - but that means every other business is getting swept up in the storm
While the lawmakers take on the multi-nationals, to force them to wake up to the slack standards they've used for securing consumer data, we have to prepare for the fallout
Is it the end of massive breaches of consumer data - like Sony, Equifax, Yahoo
While that is a good thing, fines from the General Data Protection Regulations are not just about breaches of data, but about your system for prevention and how you communicate your use of consumer data
It clarifies the rights consumers have
You should review your Privacy Policy and update it to reflect these clarifications before May
Start here:
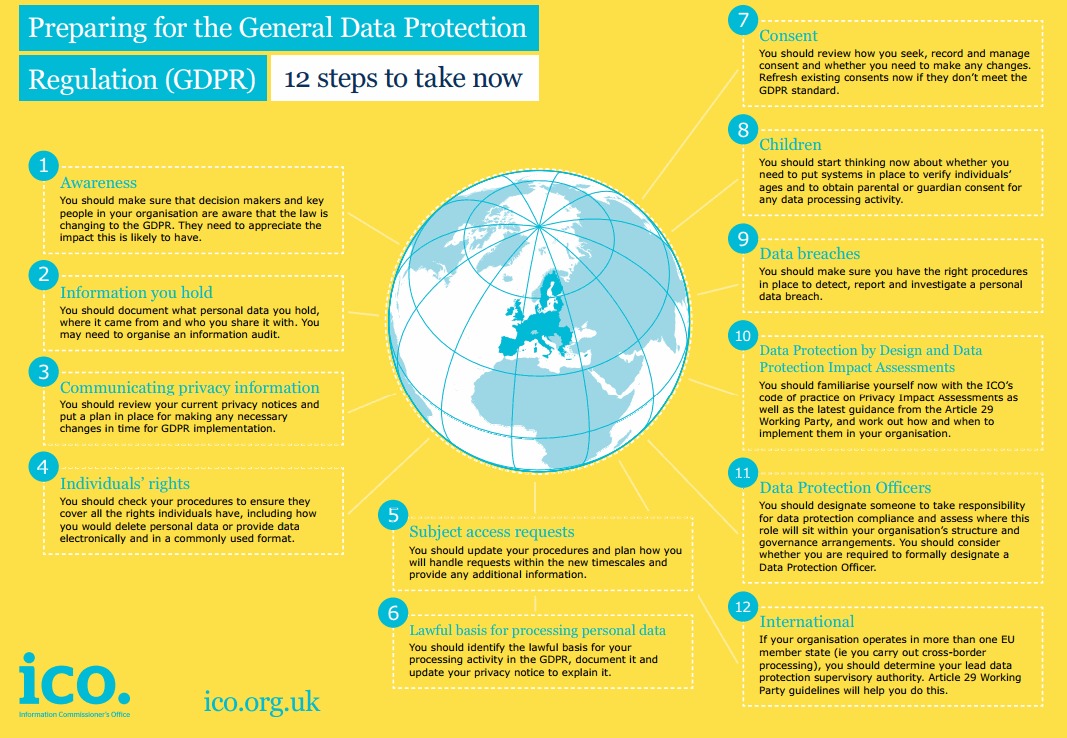
- Awareness –
organisations should be acting now to ensure they are GDPR compliant by 25 May 2018. There is less than one year to go and implementation of the GDPR within anorganisation could involve significant resources and planning – it's never too early to be prepared!! Information you hold – the GDPR requiresorganisations to maintain records of all processing activities and the legal bases for processing such data. It is important fororganisations to review the data you have, where this came from, how long you have had it and the legal basis for processing.- Communicating privacy information –
organisations should review their privacy notices and put a plan in place to make the necessary amendments to ensure GDPR compliance. The ICO has developed a code of practice for Privacy notices whichorganisations can use to ensure GDPR compliance. - Individuals rights – The ICO has updated the 12 steps to reflect the additional rights individuals will have under the GDPR:
- right to be informed;
right of access;- right to rectification;
- right to erasure;
- right to restrict processing;
- right to data portability;
- right to object; and
- right not to be subject to automated decision making and profiling.
The right to data portability is new and only applies to personal data an individual has provided to a controller where the processing was based on consent or performance of a contract and processing is carried out by automated means. You will need to provide information in a commonly used
- Subject access requests –
organisations should update policies and procedures in place to deal with subject access requests to ensure you can complywithin the newone month deadline. Lawful basis for processing personal data –organisations must review the legal bases used for processing personal data to ensure this is still relevant and will be GDPR compliant.- Consent – Where your
organisation relies on consent, you should read the ICO guidance, as this legal basis is undergoing the most change under GDPR. - Children – under the GDPR, for the first time, children's personal data will be specially protected where
organisations are offering information society services directly to children. Organisations should ensure they have processes and mechanisms in place to verify the age of users and seek parental consent for children under 13 (in the UK). - Data breaches – in certain circumstances
organisations will only have 72 hours fromdiscovery of a breach to notify the relevant data protection authority of the breach. Organisations will also have the obligation, in certain circumstances, to notify data subjects directly if the data breach is likely to result in high risk to their personal data. - Data protection by design and data protection impact assessments – PIA's will be required where processing is likely to result in high risk to individuals, e.g.
where rolling out new technology, where profiling occurs or where processing is conducted on a large scale. The ICO and the Article 29 Working Party have released guidance on this issue. - Data Protection Officers (DPO's) –
organisations should evaluate whether they requireto appoint a DPO under the GDPR. If you would like more information on this, please read our blog or read the Article 29 Working Party guidance. - International – where your
organisation operates in more than one member state, you should identify the lead supervisory authority. For more information, please see the Article 29 Working Party guidance.
Next Steps
If your site has
